Don't let your Implementation of AI be a Stochastic Parrot
AI systems rely on context to direct their actions. Anthropomorphizing AI and providing incomplete contextual clues can lead to unpredictable outcomes and can be a source of frustration for businesses. Here are some thoughts on how businesses should integrate AI, with caution against becoming a 'stochastic parrot' (as coined by Dr. Emily M. Bender).
Published: March 8, 2024
Following a few simple rules will ensure your AI solution will create meaning for all of your employees and customers, instead of generating random nonsense that merely sounds `correct`.
Introduction to AI in Business
Artificial intelligence (AI) has cemented its place as a cornerstone of innovation across various industries. Businesses are increasingly harnessing AI to streamline operations, enhance decision-making, and create new value propositions.
Generative AI is a breakthrough area, where AI systems like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) and DALL-E generate content from text to images. These technologies are revolutionizing design, content creation, and simulation. For instance, businesses use generative AI for creating marketing material, prototyping products, and simulating environments for training AI models. Here's an exploration of the multifaceted applications of AI in the business landscape:
Analytics and Data-Driven Decisions
Businesses are utilizing AI-powered analytics to turn vast amounts of data into actionable insights. Machine learning models are adept at identifying patterns and predictions that would be impossible for humans to detect within a practical timeframe. For instance, AI in retail can forecast purchasing trends, enabling stock optimization, personalized marketing, and dynamic pricing.
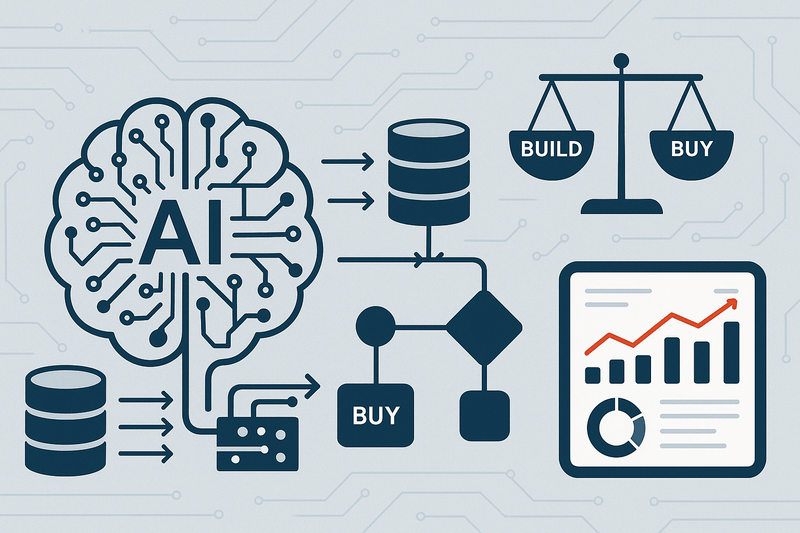
Neural Networks vs. Rules-Based Systems
AI implementation often involves a choice between neural networks and rules-based systems. Neural networks are a subset of machine learning that are modeled after the human brain and can learn from data. They excel at tasks such as image and speech recognition and are central to the development of deep learning applications.
In contrast, rules-based systems—also known as expert systems—use a set of predefined rules to make inferences or decisions. These systems are transparent and easier to troubleshoot, but they lack the learning and adaptive capabilities of neural networks. They are often used in structured environments where rules are well-defined, like compliance checking or eligibility criteria assessments.
The Outsourcing Dilemma
Deciding when and how to outsource AI capabilities is critical. Small to medium-sized enterprises may lack the resources to develop AI in-house and can benefit significantly from outsourcing to specialized vendors. Outsourcing allows businesses to adopt AI technologies without the overhead of research and development. However, it is essential for businesses to retain strategic control and understanding of the AI systems to ensure alignment with business ethics and goals.
Ethical and Practical Considerations
As businesses adopt AI, it's imperative to address the ethical implications. AI must be developed and deployed responsibly, with a focus on fairness, accountability, and transparency. This is crucial not only to prevent the perpetuation of biases but also to maintain public trust.
The Future of AI in Business
AI is not a magic solution that can solve all business challenges. Its deployment must be strategic, with a clear understanding of the strengths and limitations of different AI technologies. The goal should be to augment human abilities and to create systems that can work symbiotically with human oversight. The businesses that will thrive in the AI-driven future are those that understand how to leverage these technologies ethically and effectively, while continuously adapting to the evolving AI landscape.
Analyzing 'The Stochastic Parrot'
In her thought-provoking article, Dr. Emily M. Bender takes a contrarian approach to the current wave of AI adoption, cautioning against what she refers to as 'stochastic parrot' behavior. This term draws an analogy to parrots, which can mimic human speech but do not comprehend the meaning of the words they replicate. In the realm of artificial intelligence, this refers to AI systems that can predict, generate, and respond based on vast datasets, yet lack a genuine understanding of the content.
Recognizing Stochastic Parrots in the Wild
In human terms, a stochastic parrot is someone who repeats words or phrases without understanding their significance or context. They can give the illusion of knowledge or competence while actually just reiterating what they've heard elsewhere. It's a surface-level mimicry devoid of deeper comprehension.
Businesses face a similar risk when employing AI systems. When AI is applied to customer service, for instance, it may provide responses that are syntactically correct but semantically irrelevant or insensitive, echoing past inputs rather than engaging with present context. This reflects the AI's lack of true understanding, much like a parrot repeating human words.
An example of a business system displaying stochastic parrot behavior could be a chatbot used for customer service. If the chatbot only provides generic responses based on keywords without grasping the nuance of customer inquiries, it may give irrelevant or unhelpful answers, reflecting its inability to understand context like a human would.
Designing Systems to Avoid Stochastic Parroting
To avoid creating stochastic parrot systems, businesses need to design AI with contextual awareness and a feedback mechanism for learning. Incorporating human oversight can help ensure AI decisions are in line with ethical and practical business norms. AI systems should be seen as tools to augment human intelligence, not replace it.
Business processes need to adapt when AI is introduced. Enhanced review controls may be required to ensure data remains consistent with historical norms, that decisions have a secondary (human) review before they are implemented, and that generative systems have multiple filters to provide context and rules-based checks and balances.
When users treat generative systems as "human", their ability to effectively validate their outputs dimish. Training for both AI developers and users is essential to prevent anthropomorphizing AI systems. Users should be made aware that AI, regardless of how personable it may seem, is not sentient and does not possess human-like understanding. This understanding helps prevent overreliance on AI and encourages the use of AI as an aid rather than a decision-maker.
Next Steps
By critically engaging with these AI systems and understanding their limitations, businesses can more effectively harness the power of AI and create systems that truly add value without repeating the mistakes of the past.
Want to learn more about working with Swift?
Do you have feedback on this article or are you struggling with automating your business? We're here to help. Let's talk.